Joints
Joints by KIPP
Joints play a crucial role in mechanical engineering as they enable movements and connections between different components. They are mechanical connections that join two or more parts and simultaneously perform a movement relative to each other.
Joints also allow for transmission and redirection of forces. They can support shafts and serve as elements in cross-bracing for moving assemblies. They ensure mobility and flexibility of machines and mechanical systems. Joints are used in a wide range of applications and contribute to efficiency, flexibility and functionality of mechanical systems.
Construction of joints
A joint usually consists of several main components. These include a joint bearing, joint arms or joint axles, connecting elements such as screws or bolts and possibly additional elements such as seals or lubricants. The joint bearing is an essential component that allows for movement and absorbs loads and forces that occur during operation at the same time. Depending on the application, different types of joint bearings can be used, such as ball joints, plain bearings or universal joints.
Application areas
Joints are used in almost all fields of mechanical engineering. They play an important role in mechanical devices such as hinges for doors and hatches or couplings in drive systems. Joints are also used in medical technology, e.g. for prostheses or medical appliances.
The, for instance, enable:
- The movement of robot arms in industrial automation
- Swivelling movements of crane booms in the construction industry or
- rotational movements of axles in vehicles
Joints in the KIPP range
Joints can have different shapes and configurations. The correct selection and design of joints in mechanical engineering is crucial to ensure optimum performance and reliability.
Factors such as load capacity, freedom of movement, wear resistance and corrosion resistance must be carefully considered. In addition, regular maintenance and lubrication plays an important role in maximising service life and efficiency of the joints.
The product group "joints in mechanical engineering" includes many individual products. These are briefly described below.
Quick-fit couplings
Quick-fit couplings are mechanical connectors that enable quick and easy assembly and disassembly of components. They are usually made of steel and are available in various sizes and designs. The KIPP range includes quick-fit couplings with radial offset compensation, radial offset compensation and screw-on flange and with angular and radial offset compensation. They are often used in hydraulic and pneumatic systems to connect and disconnect components quickly without using tools.
Clevis joints
Clevis joints are connecting elements consisting of a clevis and a pin. The clevis is a U-shaped component made of metal. It is used to hold the pin to which a tang is connected and enables a swivelling connection. The Kipp clevis joints are based on DIN 71752 and are used in various applications, such as in vehicle steering and suspension systems.
Snap-in pins
A snap-in pin is a clevis pin with an attached leaf spring. They are used together with clevis joints. They are made of steel and are used to hold the pin in the clevis joint. The half-round part of the leaf spring clips around the clevis shank. Snap-in pins are often used in applications where a secure yet quick-release of the clevis joint is required, e.g. in fixtures that require regular maintenance or rebuilding. At KIPP, snap-in pins are available with a pin diameter of 4 to 16 mm.
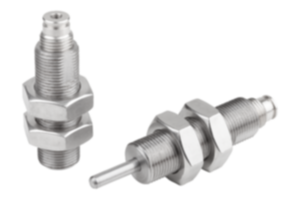
Pins
A pin is a cylindrical connecting element made of steel 1.0718 or stainless steel 1.4305. It is used to connect two or more components. Pins can be threaded or smooth and are often secured with nuts or other fastening elements.
The following pins, all suitable for clevises, are available from the KIPP range:
- pins with split pin hole
- pins with circlip groove
- pins with groove for E-type circlips
Clevises
Clevises are a part of the clevis joint. It is the U-shaped part into which the pin is inserted. Clevises are often used in steering and suspension systems to create a flexible connection between different components. KIPP clevises are available in steel or stainless steel with an external or internal thread. Snap-in pins acc. to DIN 71752 are included or available as accessories.
Clevis tangs
Clevis tangs are mating parts to clevises. They are made of steel and are mating parts that swivel on the pin and connect to opposing components. Clevis tangs are always used with a clevis and clevis pin and form the complete clevis joint.
Angle joints
Angle joints are connecting elements that enable components to be connected to each other at angle of 90°. They consist of a ball seat and a ball stud that fits into the seat. They are available in steel or stainless steel 1.4305 and are manufactured acc. to DIN 71802. Angle joints are often used in applications where a flexible connection at a specific angle is required, e.g. in steering systems or in industrial machinery.
Ball seats and ball studs
A ball seat is a component with a cup-like seating in the head. They are made from steel and are the seating for ball studs. Ball seats by KIPP are one part of an angle joint and are manufactured acc. to DIN 71805.
A ball stud is a pin with a spherical head. They are made from steel and fit into a ball seat to form a complete angle joint.
Rod-end eyes
Rod-end eyes are also connecting elements. They are a flat pin with a hole and an internal thread. They fit into a clevis to form a swivel joint and are used in many applications. KIPP rod end eyes are available made of electro zinc-plated steel or bright stainless steel 1.4305.
Circlips for ball seats
Circlips are securing elements that secure a ball stud in a ball seat. They are made of spring steel. The C shaped part fits into a groove below the ball seat head while the pin at 90° to the C fits through a hole drilled into the side of the ball seat head. Circlips are used to prevent the ball stud falling out of a ball seat acc. to DIN 71805.
Split pins and R-clips
Split pins are made of steel or stainless steel and are used to secure bolts, screws, nuts or other fastener elements. They are inserted through pre-drilled holes or slots in bolts, nuts etc. and then the ends are bent back. They are there to prevent unintentional removal or loosening.
An R-clip is a type of securing element consisting of a pin and a spring. The pin is formed into an R shape with a single or double winding. The straight pin fits through a hole and the spring form holds it in place. R-clips are often used to secure bolts, shafts or other elements.
Axial joints
Axial joints are joints that enable axial movement or displacement. They are often used in mechanical systems where linear movement in the axial direction is necessary. Axial joints consist of ball seats and ball studs in various designs and are made from steel or stainless steel.